Space launch vehicles use liquid propellant rocket engines with high-pressured turbopumps to deliver extremely low temperature propellants of liquid hydrogen, liquid nitrogen, liquid oxygen or liquid natural gas (methane) to a combustion chamber in the engine. During developmental testing of advanced turbopump designs, engineers monitor the radial and axial displacements of the rotors over the entire speed range of operation.
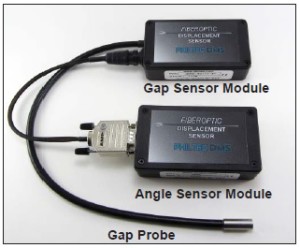
Philtec’s FODS (Fiber Optic Displacement Sensors) are being successfully used for rotor dynamics measurements in cryogenic fluids. When a fiber optic probe is submersed in a fluid, light rays diverging from the probe tip are more collimated than they would be in air. This increases the operating range of the sensor. The degree of collimation is proportional to the index of refraction of the fluid.
Refractive Index of Common Cryogenic Fluids
1.0002926 Air
1.0974 Liquid Hydrogen
1.2053 Liquid Nitrogen
1.221 Liquid Oxygen
1.286 Liquid Natural Gas (Methane)
OPERATION IN CRYOGENIC FLUID, EXAMPLE
Philtec provides the rocket engineers with a calculated best estimate of sensor performance following this example:
- calibrate the displacement sensor in air (or water), then
- rescale the gap data to derive an estimate of the sensor output in the cryo fluid.
For example, a sensor is calibrated to a target surface in Air with Refractive index of 1.0002926
For a probe immersed in Liquid Hydrogen with Refractive index of 1.0974, the sensor’s calibration gap data is scaled by the ratio of the Refractive Indices:
1.0974 ÷ 1.0002926 = 1.0971
Two calibration charts are provided: One for operation in Air; one for operation in LH2
Example Chart_LH2
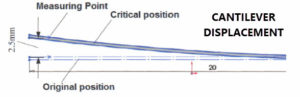 Sensor probes are to be generally mounted normal (perpendicular) to a target surface. With some applications, such as displacement of a cantilever beam, the target surface rotates as deflects. In other applications, due to installation constraints, the probe can not be mounted normal to the surface. In applications where tilt is unavoidable, what sensors can be used?
Sensor probes are to be generally mounted normal (perpendicular) to a target surface. With some applications, such as displacement of a cantilever beam, the target surface rotates as deflects. In other applications, due to installation constraints, the probe can not be mounted normal to the surface. In applications where tilt is unavoidable, what sensors can be used?